The Year of the Comets: Three Reasons Why 2013 Could be the Best Ever:
The Year of the Comets: Three Reasons Why 2013 Could be the Best Ever
by BOB KING on FEBRUARY 19, 2013
Want to stay on top of all the space news? Follow @universetoday on Twitter

Comet L4 Panstarrs photographed from Australia at dawn on Feb. 17, 2013 with a telephoto lens. A bright head and short tail are visible. Credit: Joseph Brimacombe
2013 could turn out to be a comet bonanza. No fewer than three of these long-tailed beauties are expected to brighten to naked eye visibility. Already Comet C/2011 L4 PANSTARRS has cracked that barrier. Sky watchers in Australia have watched it grow from a telescopic smudge to a beautiful binocular sight low above the horizon at both dusk and dawn. A few have even spotted it without optical aid in the past week. Excited reports of a bright, fan-shaped dust tail two full moon diameters long whet our appetite for what’s to come.
Recent brightness estimates indicate that the comet could be experiencing a surge or “second wind” after plateauing in brightness the past few weeks. If the current trend continues, PanSTARRS might reach 1st or 2nd magnitude or a little brighter than the stars of the Big Dipper when it first becomes visible to northern hemisphere sky watchers around March 7. That’s little more than two weeks away!
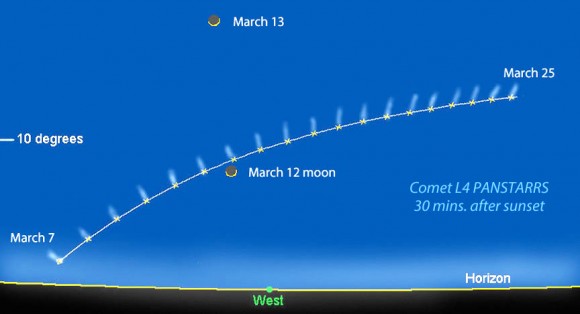
Comet Panstarrs will make its first appearance for northern hemisphere sky watchers around March 7 low in the western sky after sundown. Notice that the comet gets no higher than 10 degrees – about one fist held at arm’s length – through much of the month. Illustration created using Chris Marriott’s SkyMap software
Every day between now and March 10, when PanSTARRS’ orbit takes it closest to the sun, the comet is expected to slowly increase in brightness. Later this month it disappears in the solar glare, but when it re-emerges into evening twilight around Thursday, March 7, northern and southern hemisphere observers alike will get great views. Binoculars should easily show a bright head and swept-back tail pointing away from the sun. And don’t forget to mark your calendar for March 12. On that date the thin lunar crescent will join the comet for a rare photogenic pairing. To locate and keep track of PanSTARRS, you’ll need the following materials and circumstances:
* An unobstructed view of the western horizon
* Clear, haze-free skies at dusk
* Pair of binoculars
* A map
I can’t help you with all of the above, but this map will help point you in the right direction. Once you find a location with a great western view, watch just above the horizon for a fuzzy, star-like object in your binoculars. While it’s possible the comet will be bright enough to see with the naked eye, binoculars will make finding it much easier. They’ll also reveal details of tail structure too subtle to be visible otherwise.

Incredible detail is seen in the gas tail of F6 Lemmon in this photo made with a 19.6-inch telescope Feb. 17, 2013. Credit: Martin Mobberley
Comet PanSTARRS has some cometary company. C/2012 F6 Lemmon is currently plying its way through the constellation Tucana the Toucan, shining right around the naked eye limit at magnitude 5.5. To the unaided eye, Lemmon looks like a dim fuzzy spot. Binoculars show a thin gas tail and big, bright head or coma. Comas develop around the comet’s icy nucleus as sunlight vaporizes dusty ice to create a short-lived atmosphere that in the shape of a luminous teardrop. Long-exposures like the one above reveal richly-detailed streamers of carbon monoxide and other gases fluorescing in sunlight in the comet’s fashionably skinny tail.
Lemmon is slowly receding from Earth this month, but should remain just above the naked eye limit for some time as it continues to approach the sun. Northern hemisphere observers will need to be patient to see this one. After looping around the sun on March 24, the comet will pop back into the morning sky near the familiar Square of Pegasus asterism in early May. If we’re lucky, Lemmon may still be near the naked eye limit and visible in ordinary binoculars.

Cmet C/2012 F6 (Lemmon), imaged on
Feb. 19. 2013 remotely from Q62 (iTelescope Observatory, Siding Spring). Credit: Ernesto Guido and Nick Howes, Remanzacco Observatory.
Before we move on to the comet with the greatest expectations, I want to mention Comet 2P/Encke. Encke was the only the second comet to have its orbit computed – way back in 1819 by German astronomer Johann Encke. This year it’s making its 62nd observed return to Earth’s vicinity. That’s a lot of visits, but when your orbital period is only 3.3 years – the shortest known of any comet – you can’t help but be a regular visitor. While not expected to brighten to naked eye level, the comet will be a fine sight in modest-sized telescopes glowing around 8th magnitude when it tracks between the Big Dipper and Leo the Lion this October.
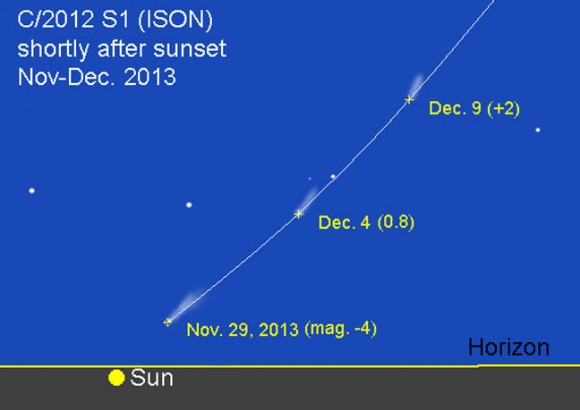
Comet ISON in the western sky shortly after sunset in late November this year. Illustration created with Chris Marriott’s SkyMap software
Our final comet, Comet C/2012 S1 ISON, was discovered last September by Russian amateurs Vitali Nevski and Artyom Novichonok while making observations for the International Scientific Optical Network (ISON). At the time, it was farther than Jupiter and impossibly faint, but once ISON’s orbit was determined, astronomers realized the comet would pass only 1.1 million miles from center of the sun (680,000 miles above its surface) on November 28, 2013.
Comet ISON belongs to a special category of comets called sungrazers. As the comet performs a hairpin turn around the sun on that date, its ices will vaporize furiously in the intense solar heat. Assuming it defies death by evaporation, ISON is expected to become a brilliant object perhaps 10 times brighter than Venus. Or brighter. Some predict it could put the full moon to shame. If so, that would occur for a brief time around at perihelion (closest approach to the sun) when the comet would only be visible in the daytime sky very close to the sun. When safely viewed, ISON might look like a brilliant, fuzzy star in a blue sky.
Most of us won’t risk burning our retinas staring so close to sun. Instead we’ll watch with anticipation as the comet sprouts a long tail while ascending from the western horizon just after sunset in late November and early December. Whatever it does, sky watchers in both southern and northern hemispheres will ringside seats when ISON’s at its best.
Right now the comet’s whiling away its time in the constellation Gemini the Twin and still very faint. Come September, it should be easily visible in small telescopes in the morning sky. The first naked eye sightings could happen in late October. Many of us hope the comet will be one for the record books, a worthy successor to C/2006 P1 McNaught, the last “great comet” to dazzle human eyes. It reached peak magnificence for southern hemisphere sky watchers in January 2007.

C/2006 P1 McNaught became a memorable sight for observers living in southern latitudes in January 2007. Will Comet ISON do the same? Credit: Wikipedia
Three bright comets – and one modestly bright – might be enough for a year, but there could be surprises. Dozens of new comets are discovered each year by professional sky surveys and amateur astronomers. Most are faint and move along their appointed paths unnoticed by 99.9% of the world’s population, but every so often a new one comes along that blossoms into a spectacle. How many of those are out there tonight waiting to be discovered?
Read more: http://www.universetoday.com/100049/the-year-of-the-comets-three-reasons-why-2013-could-be-the-best-ever/#ixzz2LRCGl000
More here: The Year of the Comets: Three Reasons Why 2013 Could be the Best Ever

